Dijkstra最短路径¶
1 定义¶
Dijkstra 算法允许我们在图的任意两个顶点之间找到最短路径,它不同于最小生成树,因为两个顶点之间的最短距离可能不包括图的所有顶点。
2 Dijkstra 最短路径工作步骤¶
Dijkstra 算法的工作原理是,顶点 A 和 D 之间的最短路径 A->D 的任何子路径 B->D 也是顶点 B 和 D 之间的最短路径。
Djikstra 在相反的方向使用了这个属性,即我们高估了每个顶点到起始顶点的距离。然后我们访问每个节点及其相邻节点,以找到最短子路径。
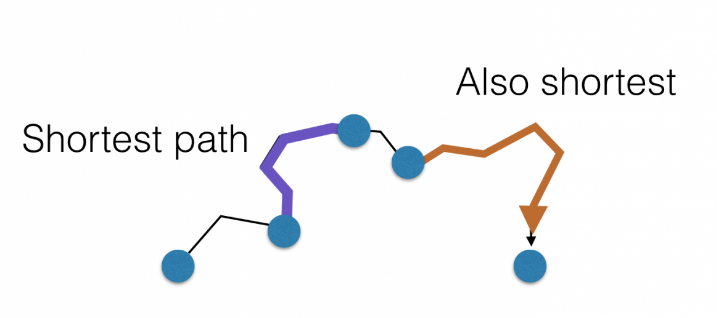
该算法使用贪婪的方法,即我们寻找下一个最佳解,希望最终结果是整个问题的最佳解。
3 Dijkstra 最短路径算法示例¶
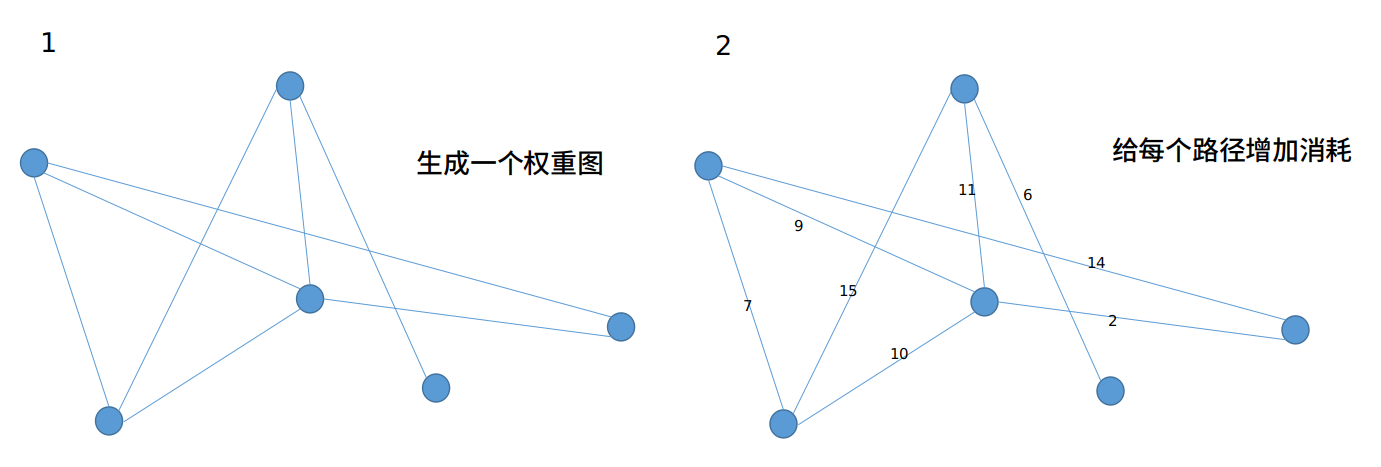
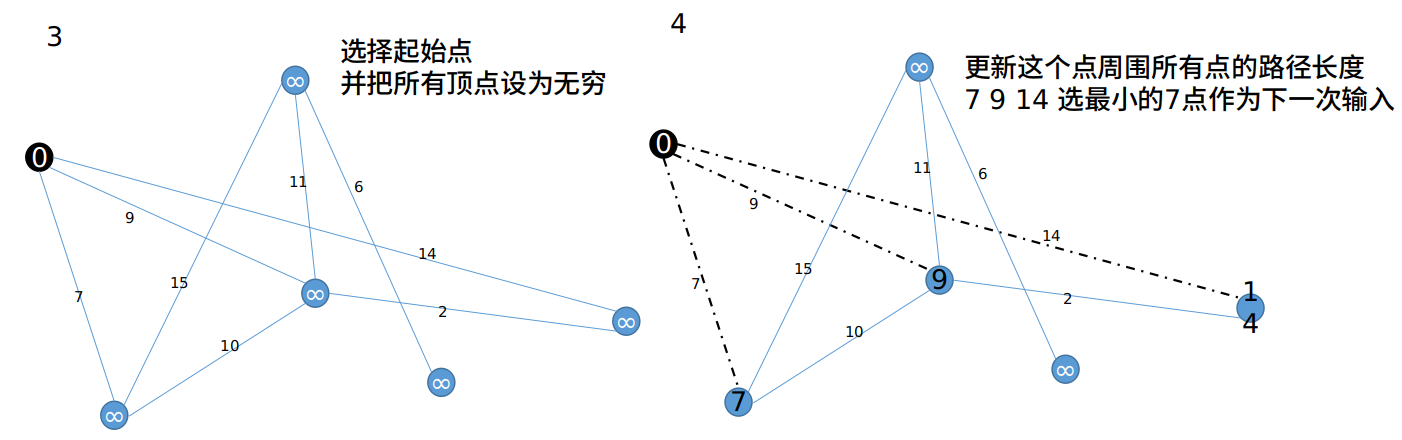
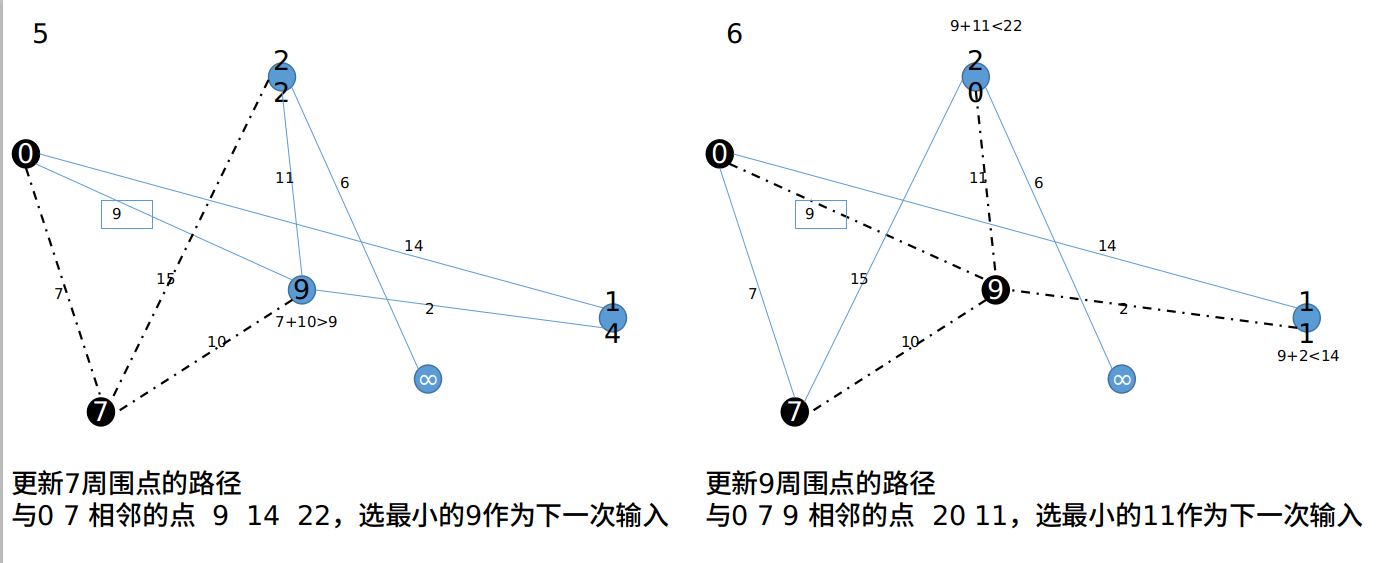
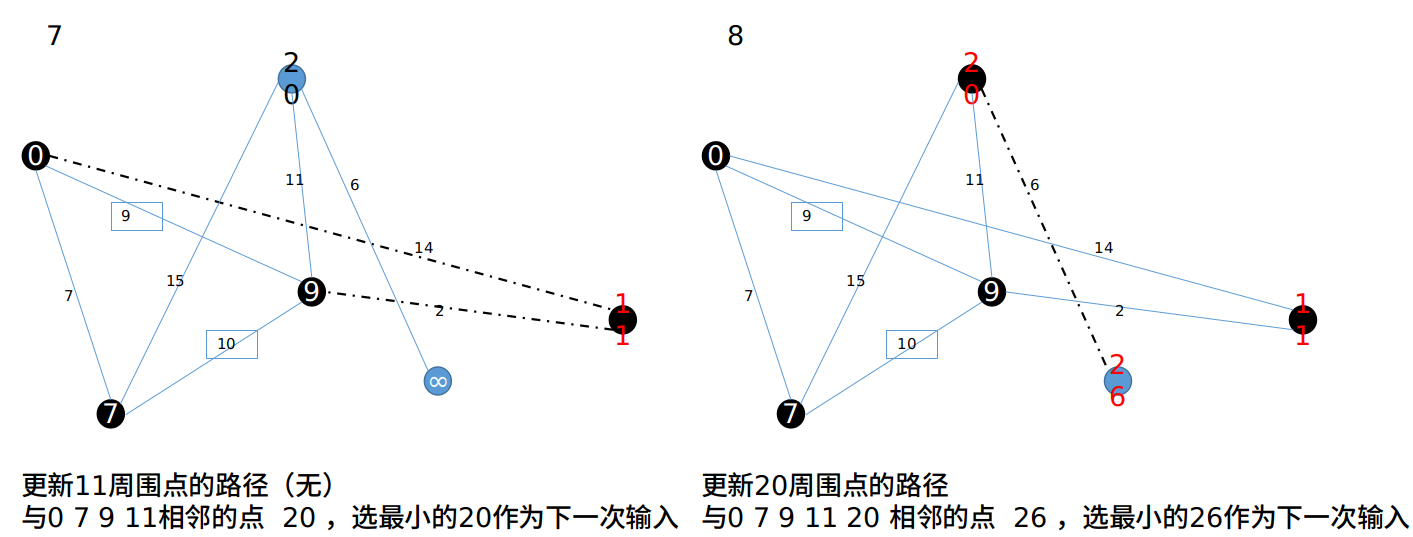
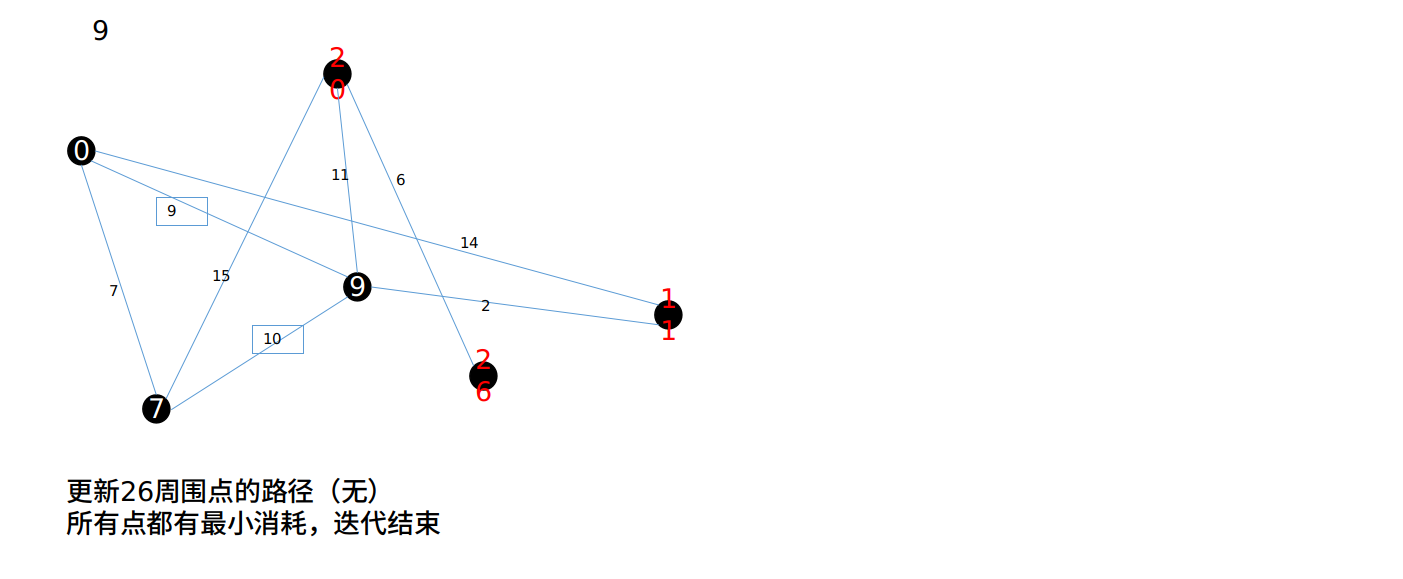
4 算法优化¶
百度可以找到很多 Dijkstra 最短路径的代码,总是初始化两个矩阵,一个路径矩阵、一个点是否检测矩阵。
这样做增加了很大的内存和时间,我测试案例权重图比较大,84 个平面,每个平面 1000+个点,结果按照使用初始化矩阵图的形式,内存占了 20 多 g,时间也超长,完全没法搞。
其实很多时候大家只是找一个点到另一个点的距离,不需要到所有点的距离。那我们只要找初始点到末位点就可以了。程序也不要搞一个初始化矩阵,每个点建立一个类,存放相关信息比较靠谱。
5 优化程序¶
实现输入超大数据,快速找最短路径。单点对单点。
程序讲解
Node:节点类
Size_t get_pos () const 返回节点编号
Size_t node_pos_ 节点编号
Adjacent_nodes_ 相邻节点编号
Adjacent_weights_ 相邻节点权重
Shortest_path_ 最短路径
Visited 是否被访问
Parent_node 父节点
rule:multiset 的重载结构体,包括比较函数。用于 multiset 的排序
Graph:网络图
Get_node 返回对应节点
Num_verticies_ 网络下节点数量
V_ 网络下节点集
Dijkstra_SP 寻找最短路径
Recover_Path 打印路径
#include <iostream>
#include <tuple>
#include "../Graph.h"
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
Graph G_test(6);
G_test.V_[0].adjacent_nodes_ = vector<size_t> {1, 2, 5};
G_test.V_[0].adjacent_weights_ = vector<uint64_t> {7, 9, 14};
G_test.V_[1].adjacent_nodes_ = vector<size_t> {0, 2, 3};
G_test.V_[1].adjacent_weights_ = vector<uint64_t> {7, 10, 15};
G_test.V_[2].adjacent_nodes_ = vector<size_t> {0, 1, 3, 5};
G_test.V_[2].adjacent_weights_ = vector<uint64_t> {9, 10, 11, 2};
G_test.V_[3].adjacent_nodes_ = vector<size_t> {1, 2, 4};
G_test.V_[3].adjacent_weights_ = vector<uint64_t> {15, 11, 6};
G_test.V_[4].adjacent_nodes_ = vector<size_t> {3, 5};
G_test.V_[4].adjacent_weights_ = vector<uint64_t> {6, 9};
G_test.V_[5].adjacent_nodes_ = vector<size_t> {0, 2, 4};
G_test.V_[5].adjacent_weights_ = vector<uint64_t> {14, 2, 9};
size_t src_node_pos = 0;
size_t dst_node_pos = 5;
uint64_t sp = 0;
bool found = false;
std::tie(sp, found) = Dijkstra_SP(G_test, src_node_pos, dst_node_pos);
if (found) {
list<Node> path = Recover_Path(G_test, src_node_pos, dst_node_pos);
cout << "Shortest path len : " << sp << endl;
cout << "Shortest path : ";
for(list<Node>::iterator it = path.begin(); it != path.end(); it++) {
cout << it->get_pos();
}
cout << endl;
} else {
cout << "No path found.\n" << endl;
}
cout << "done" << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <limits>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <tuple>
using namespace std;
#ifndef GRAPH_H_
#define GRAPH_H_
class Node {
public:
Node() {
}
size_t get_pos() const;// 返回节点编号
size_t node_pos_ = 0;// 节点编号
vector<size_t> adjacent_nodes_;// 相邻节点编号
vector<uint64_t> adjacent_weights_;// 相邻节点权重
uint64_t shortest_path_ = std::numeric_limits<uint64_t>::max();// 最短路径
bool visited = false;// 是否被访问
Node *parent_node = nullptr;// 父节点
};
class Graph {
public:
Graph(size_t num_verticies);
Node &get_node(size_t node_pos);// 返回对应节点
~Graph() {}
size_t num_verticies_;// 网络下节点数量
vector<Node> V_;// 网络下节点集
};
std::tuple<uint64_t, bool> Dijkstra_SP(
Graph &G, size_t src_node_pos, size_t dst_node_pos);// 寻找最短路径
list<Node> Recover_Path(
Graph &G, size_t src_node_pos, size_t dst_node_pos);// 打印路径
#endif
#include <random>
#include <limits>
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include "Graph.h"
struct rule {
bool operator()(const Node &n1, const Node &n2) {
return n1.shortest_path_ < n2.shortest_path_;
}
};
Graph::Graph(size_t num_verticies) {
num_verticies_ = num_verticies;
V_ = vector<Node>(num_verticies);
for (size_t i = 0; i < num_verticies; i++) {
V_[i].node_pos_ = i;
}
}
Node &Graph::get_node(size_t node_pos) {
return V_[node_pos];
}
size_t Node::get_pos() const {
return node_pos_;
}
std::tuple<uint64_t, bool> Dijkstra_SP(
Graph &G, size_t src_node_pos, size_t dst_node_pos) {
// 初始化路径矩阵
for (vector<Node>::iterator it = G.V_.begin(); it != G.V_.end(); ++it) {
it->shortest_path_ = numeric_limits<uint64_t>::max();
it->visited = false;
}
// 初始点
Node &start_node = G.get_node(src_node_pos);
start_node.shortest_path_ = 0;
start_node.visited = true;
std::multiset<Node, rule> frontier;
frontier.insert(start_node);
// 没有找到结束节点时
while (!G.get_node(dst_node_pos).visited) {
if (frontier.empty()) {
return std::make_tuple(0, false);
}
// 获取边界中最近的节点
multiset<Node, rule>::iterator nearest_node_it = frontier.begin();
Node &nearest_node = G.get_node(nearest_node_it->node_pos_);
frontier.erase(nearest_node_it);
nearest_node.visited = true;
// 如果我们找到路径它是最短的路径
if (nearest_node.get_pos() == dst_node_pos) {
return std::make_tuple(nearest_node.shortest_path_, true);
}
// 处理所有相邻节点
for (size_t i = 0; i < nearest_node.adjacent_nodes_.size(); i++) {
Node &node = G.get_node(nearest_node.adjacent_nodes_[i]);
// 如果已经访问过节点,则跳过它
if (node.visited == false) {
// 计算到节点的新的最短距离
uint64_t current_sp = nearest_node.shortest_path_ +
nearest_node.adjacent_weights_[i];
// 如果新计算出的路径较短,则之前计算出的路径
if(current_sp < node.shortest_path_) {
// 查找此节点是否在边境
multiset<Node, rule>::iterator ret = frontier.find(node);
// 如果是,我们找到较短的路径,则在多集中更新此节点的路径和位置
if (ret != frontier.end()) {
frontier.erase(ret);
}
// 我们发现到该节点的路径较短
node.shortest_path_ = current_sp;
node.parent_node = &nearest_node;
// 更新多集节点
frontier.insert(node);
}
}
}
}
return std::make_tuple(0, false);
}
list<Node> Recover_Path(Graph &G, size_t src_node_pos, size_t dst_node_pos) {
list<Node> path;
Node &src_node = G.get_node(src_node_pos);
Node &cur_node = G.get_node(dst_node_pos);
// 从目标节点开始恢复路径
while(cur_node.get_pos() != src_node.get_pos()) {
path.push_front(cur_node);
cur_node = *cur_node.parent_node;
}
path.push_front(src_node);
return path;
}
6 复杂度¶
优化后复杂度 n*m