装配体Assembly¶
昨天晚上实现了一个可拖动的坐标轴MovableAxesWidget,今天给他加个使用场景。准备做一个简单的机械臂运动学仿真程序。
模型用的HIWIN的机械臂,官网可以下载到模型。hiwin
毕业第一份工作就是用的HIWIN的机械臂,做个demo首先想到的就是这个。
1 vtkAssembly使用(Python)¶
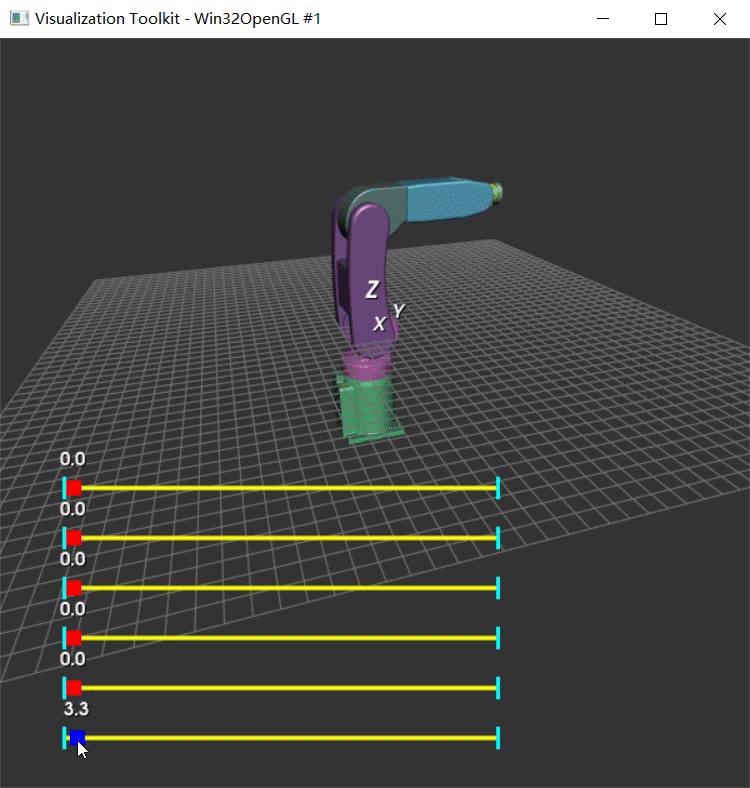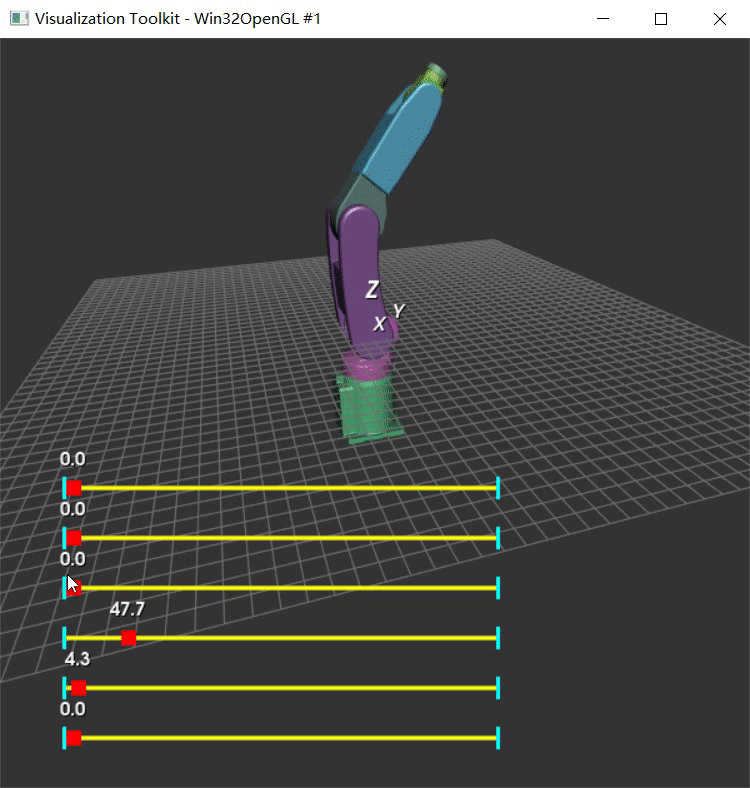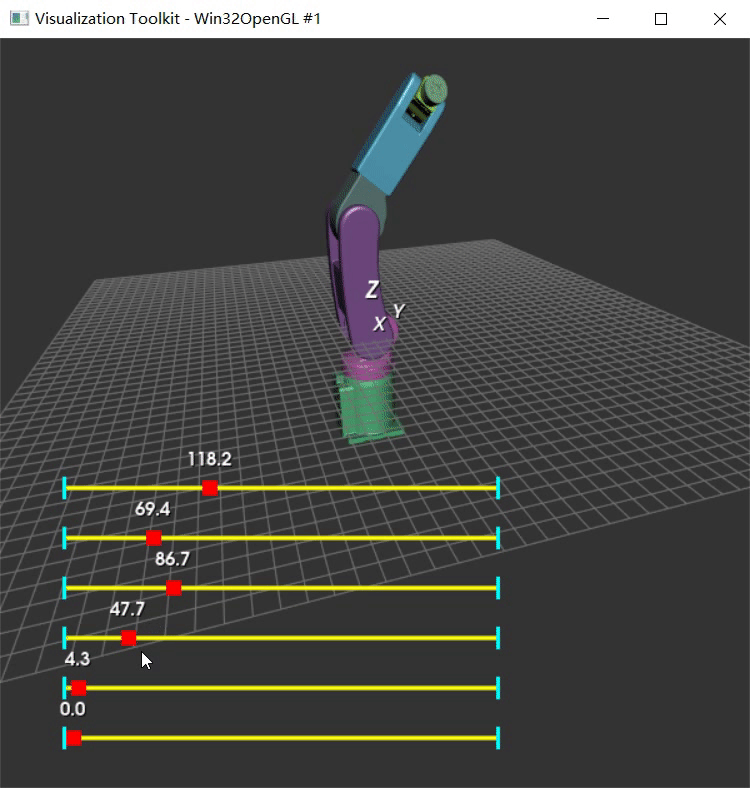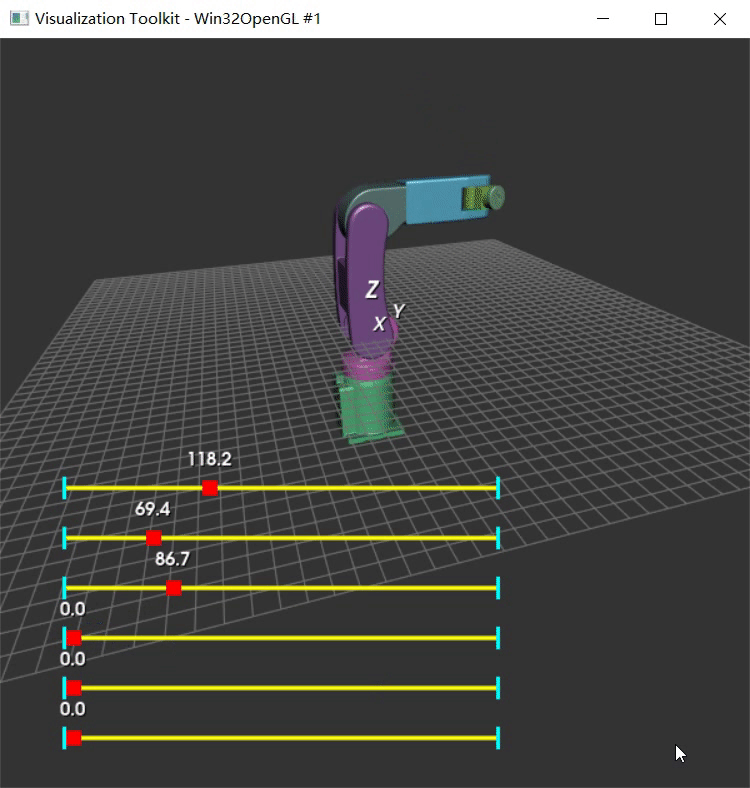
以前没用过vtkAssembly,先用Python实现下心里有谱。参考VTK中的装配体(vtkAssembly)这篇博客中的代码。
#!/usr/bin/env python
import vtk
import math
from vtk.util.colors import *
filenames = ["RA605_0.stl", "RA605_1.stl", "RA605_2.stl",
"RA605_3.stl", "RA605_4.stl", "RA605_5.stl", "RA605_6.stl"]
dt = 1.0
angle = [0, 0]
renWin = vtk.vtkRenderWindow()
assemblys = list()
slider_shoulder = vtk.vtkSliderRepresentation2D()
slider_elbow = vtk.vtkSliderRepresentation2D()
actor = list()
class MyInteractor(vtk.vtkInteractorStyleTrackballCamera):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
self.AddObserver("CharEvent", self.OnCharEvent)
self.AddObserver("KeyPressEvent", self.OnKeyPressEvent)
def OnCharEvent(self, obj, event):
pass
def OnKeyPressEvent(self, obj, event):
return
def LoadSTL(filename):
reader = vtk.vtkSTLReader()
reader.SetFileName(filename)
mapper = vtk.vtkPolyDataMapper()
mapper.SetInputConnection(reader.GetOutputPort())
actor = vtk.vtkLODActor()
actor.SetMapper(mapper)
return actor
def CreateCoordinates():
axes = vtk.vtkAxesActor()
axes.SetTotalLength(100, 100, 100)
axes.SetShaftType(0)
axes.SetCylinderRadius(0.02)
axes.GetXAxisCaptionActor2D().SetWidth(0.03)
axes.GetYAxisCaptionActor2D().SetWidth(0.03)
axes.GetZAxisCaptionActor2D().SetWidth(0.03)
return axes
def SliderCallback1(obj, event):
sliderRepres = obj.GetRepresentation()
pos = sliderRepres.GetValue()
assemblys[1].SetOrientation(0, 0, pos)
renWin.Render()
def SliderCallback2(obj, event):
sliderRepres = obj.GetRepresentation()
pos = sliderRepres.GetValue()
assemblys[2].SetOrientation(pos, 0, 0)
renWin.Render()
def SliderCallback3(obj, event):
sliderRepres = obj.GetRepresentation()
pos = sliderRepres.GetValue()
assemblys[3].SetOrientation(pos, 0, 0)
renWin.Render()
def SliderCallback4(obj, event):
sliderRepres = obj.GetRepresentation()
pos = sliderRepres.GetValue()
assemblys[4].SetOrientation(0, pos, 0)
renWin.Render()
def SliderCallback5(obj, event):
sliderRepres = obj.GetRepresentation()
pos = sliderRepres.GetValue()
assemblys[5].SetOrientation(pos, 0, 0)
renWin.Render()
def SliderCallback6(obj, event):
sliderRepres = obj.GetRepresentation()
pos = sliderRepres.GetValue()
assemblys[6].SetOrientation(0, pos, 0)
renWin.Render()
def GenterSliderRep(iren, position):
slider_widget = ConfigSlider(
vtk.vtkSliderRepresentation2D(), position)
slider_widget.SetInteractor(iren)
slider_widget.EnabledOn()
return slider_widget
def ConfigSlider(sliderRep, Yaxes):
sliderRep.SetMinimumValue(0.0)
sliderRep.SetMaximumValue(360.0)
sliderRep.SetValue(0.0) # Specify the current value for the widget
# Change the color of the knob that slides
sliderRep.GetSliderProperty().SetColor(1, 0, 0)
# Change the color of the knob when the mouse is held on it
sliderRep.GetSelectedProperty().SetColor(0, 0, 1)
sliderRep.GetTubeProperty().SetColor(1, 1, 0) # Change the color of the bar
# Change the color of the ends of the bar
sliderRep.GetCapProperty().SetColor(0, 1, 1)
# sliderRep.GetTitleProperty().SetColor(1,0,0) # Change the color of the text displaying the value
# Position the first end point of the slider
sliderRep.GetPoint1Coordinate().SetCoordinateSystemToDisplay()
sliderRep.GetPoint1Coordinate().SetValue(50, Yaxes)
# Position the second end point of the slider
sliderRep.GetPoint2Coordinate().SetCoordinateSystemToDisplay()
sliderRep.GetPoint2Coordinate().SetValue(400, Yaxes)
# Specify the length of the slider shape.The slider length by default is 0.05
sliderRep.SetSliderLength(0.02)
# Set the width of the slider in the directions orthogonal to the slider axis
sliderRep.SetSliderWidth(0.02)
sliderRep.SetTubeWidth(0.005)
sliderRep.SetEndCapWidth(0.03)
sliderRep.ShowSliderLabelOn() # display the slider text label
sliderRep.SetLabelFormat("%.1f")
sliderWidget = vtk.vtkSliderWidget()
sliderWidget.SetRepresentation(sliderRep)
sliderWidget.SetAnimationModeToAnimate()
return sliderWidget
def CreateGround():
# create plane source
plane = vtk.vtkPlaneSource()
plane.SetXResolution(50)
plane.SetYResolution(50)
plane.SetCenter(0, 0, 0)
plane.SetNormal(0, 0, 1)
# mapper
mapper = vtk.vtkPolyDataMapper()
mapper.SetInputConnection(plane.GetOutputPort())
# actor
actor = vtk.vtkActor()
actor.SetMapper(mapper)
actor.GetProperty().SetRepresentationToWireframe()
actor.GetProperty().SetColor(light_grey)
transform = vtk.vtkTransform()
transform.Scale(2000, 2000, 1)
actor.SetUserTransform(transform)
return actor
def CreateScene():
# Create a rendering window and renderer
ren = vtk.vtkRenderer()
#renWin = vtk.vtkRenderWindow()
renWin.AddRenderer(ren)
# Create a renderwindowinteractor
iren = vtk.vtkRenderWindowInteractor()
iren.SetRenderWindow(renWin)
style = MyInteractor()
style.SetDefaultRenderer(ren)
iren.SetInteractorStyle(style)
for id, file in enumerate(filenames):
actor.append(LoadSTL(file))
# actor[id].GetProperty().SetColor(blue)
r = vtk.vtkMath.Random(.4, 1.0)
g = vtk.vtkMath.Random(.4, 1.0)
b = vtk.vtkMath.Random(.4, 1.0)
print(r, g, b)
actor[id].GetProperty().SetDiffuseColor(r, g, b)
actor[id].GetProperty().SetDiffuse(.8)
actor[id].GetProperty().SetSpecular(.5)
actor[id].GetProperty().SetSpecularColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
actor[id].GetProperty().SetSpecularPower(30.0)
tmp_assembly = vtk.vtkAssembly()
assemblys.append(tmp_assembly)
assemblys[id].AddPart(actor[id])
assemblys[id].SetPosition(0, 0, 0)
if(id > 0):
assemblys[id-1].AddPart(tmp_assembly)
assemblys[0].SetOrigin(0,0,375)
assemblys[1].SetOrigin(0,0,0)
assemblys[2].SetOrigin(0,30,0)
assemblys[3].SetOrigin(0,30,340)
assemblys[4].SetOrigin(0,0,380)
assemblys[5].SetOrigin(0,368,380)
assemblys[6].SetOrigin(0,368,380)
ren.AddActor(assemblys[0])
# Add coordinates
axes = CreateCoordinates()
ren.AddActor(axes)
# Add ground
ground = CreateGround()
ren.AddActor(ground)
slider_1 = GenterSliderRep(iren,40)
slider_2 = GenterSliderRep(iren,80)
slider_3 = GenterSliderRep(iren,120)
slider_4 = GenterSliderRep(iren,160)
slider_5 = GenterSliderRep(iren,200)
slider_6 = GenterSliderRep(iren,240)
slider_1.AddObserver("InteractionEvent", SliderCallback1)
slider_2.AddObserver("InteractionEvent", SliderCallback2)
slider_3.AddObserver("InteractionEvent", SliderCallback3)
slider_4.AddObserver("InteractionEvent", SliderCallback4)
slider_5.AddObserver("InteractionEvent", SliderCallback5)
slider_6.AddObserver("InteractionEvent", SliderCallback6)
# Set background color
ren.SetBackground(.2, .2, .2)
# Set window size
renWin.SetSize(600, 600)
# Set up the camera to get a particular view of the scene
camera = vtk.vtkCamera()
camera.SetFocalPoint(300, 0, 0)
camera.SetPosition(300, -400, 350)
camera.ComputeViewPlaneNormal()
camera.SetViewUp(0, 1, 0)
camera.Zoom(0.4)
ren.SetActiveCamera(camera)
# Enable user interface interactor
iren.Initialize()
iren.Start()
if __name__ == "__main__":
CreateScene()
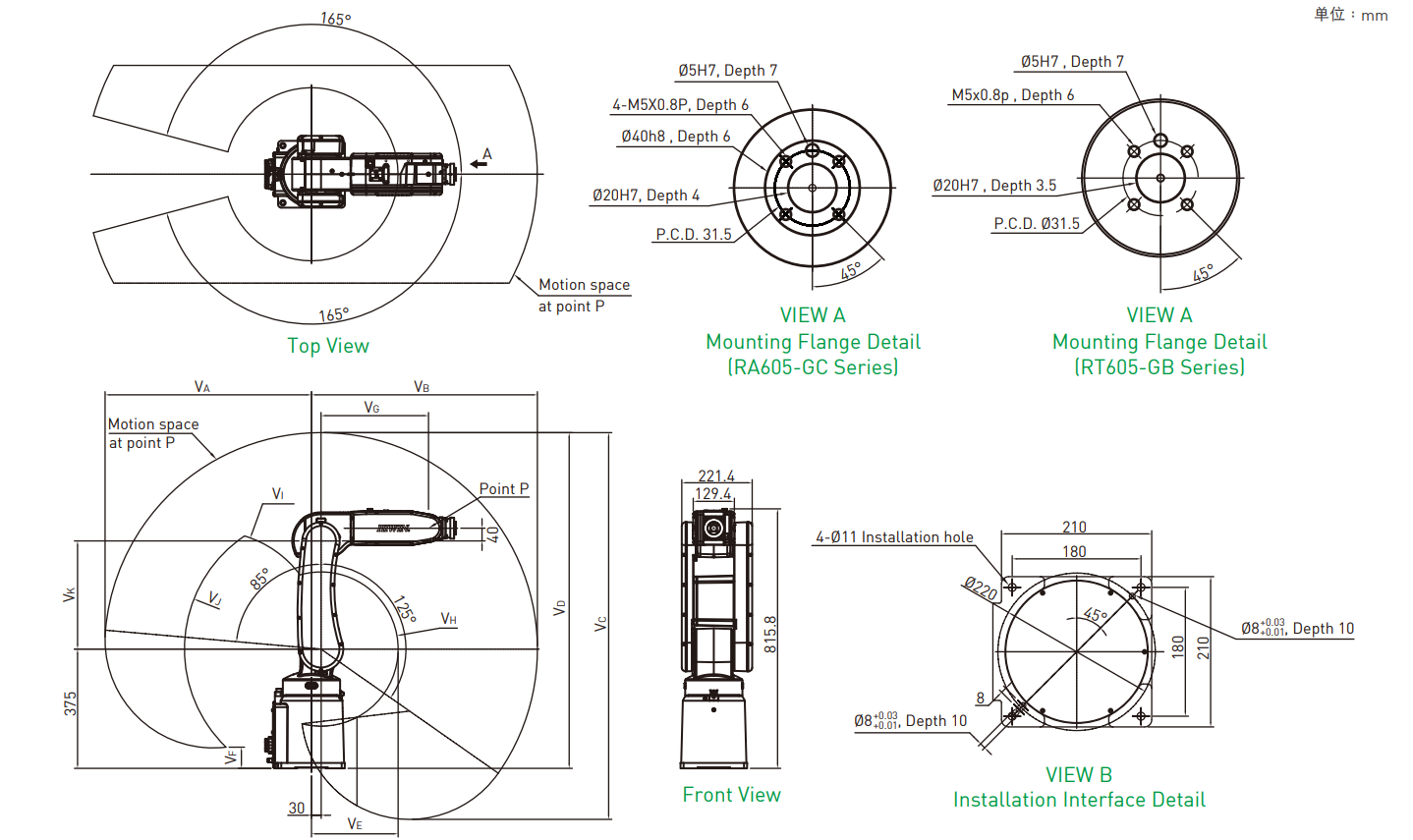
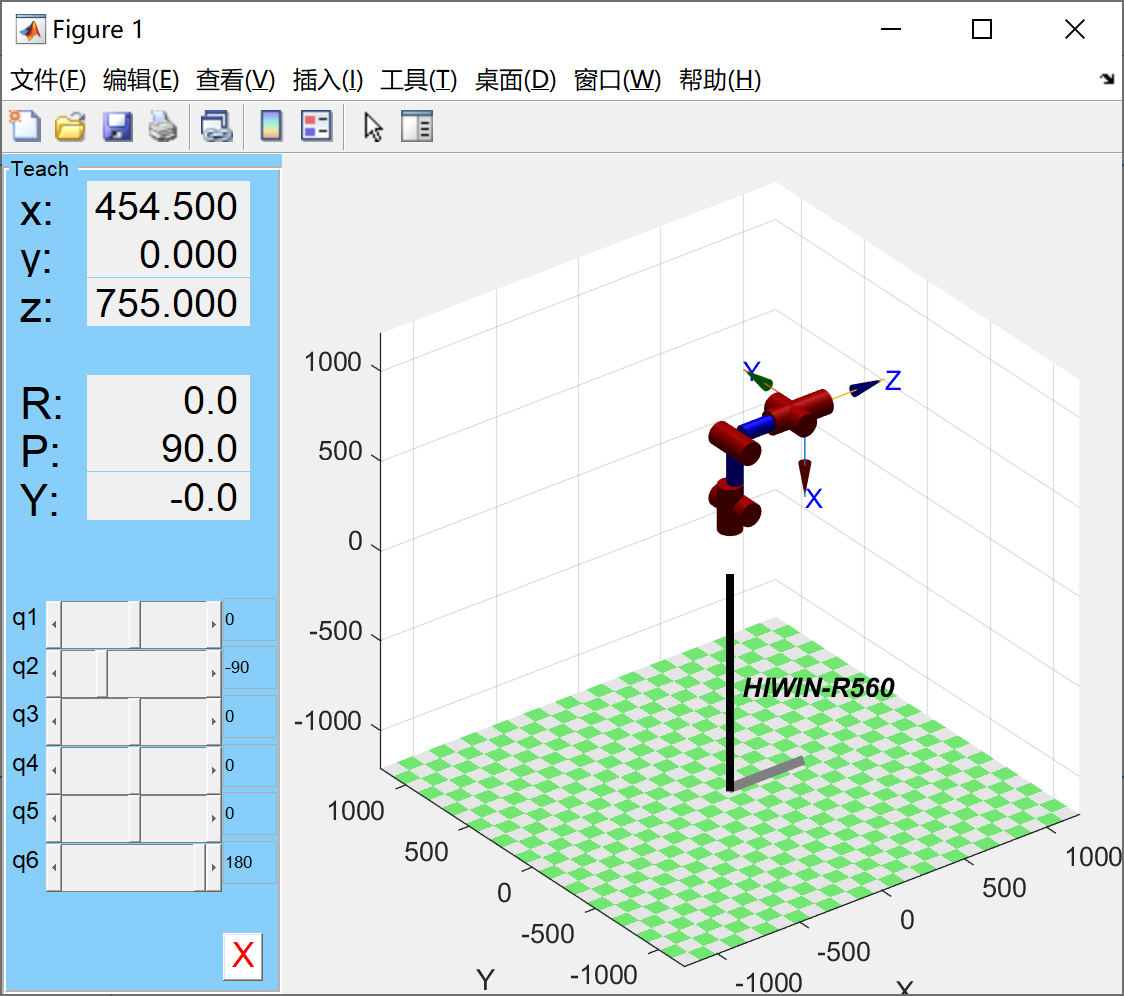
2 运动学建模¶
不考虑动力学,运动学比较简单。做一个DEMO我只需要DH参数、正解方程、逆解方程即可。
HIWIN官网也可以下载到图纸,算一下dh参数。跟matlab算的结果比较下就可以验证DH、正解找的是否正确。
clear;
clc;
close all;
%% 建模
th(1) = 0; dh_d(1) = 375; dh_a(1) = 0; alp(1) = 0;
th(2) = 0; dh_d(2) = 0; dh_a(2) = 30; alp(2) = -pi/2;
th(3) = 0; dh_d(3) = 0; dh_a(3) = 340; alp(3) = 0;
th(4) = 0; dh_d(4) = 338; dh_a(4) = 40; alp(4) = -pi/2;
th(5) = 0; dh_d(5) = 0; dh_a(5) = 0; alp(5) = pi/2;
th(6) = 0; dh_d(6) = 86.5; dh_a(6) = 0; alp(6) = -pi/2;
L1 = Link([th(1), dh_d(1), dh_a(1), alp(1), 0], 'modified');
L2 = Link([th(2), dh_d(2), dh_a(2), alp(2), 0], 'modified');
L3 = Link([th(3), dh_d(3), dh_a(3), alp(3), 0], 'modified');
L4 = Link([th(4), dh_d(4), dh_a(4), alp(4), 0], 'modified');
L5 = Link([th(5), dh_d(5), dh_a(5), alp(5), 0], 'modified');
L6 = Link([th(6), dh_d(6), dh_a(6), alp(6), 0], 'modified');
robot = SerialLink([L1,L2,L3,L4,L5,L6]);
robot.name='HIWIN-R560';
robot.display();
%% 正解
theta = [0, -90, 0,0,0,180]*pi/180;
robot.teach();
robot.plot(theta);
t0 = robot.fkine(theta) %末端执行器位姿
3 vtkAssembly使用(C++)¶
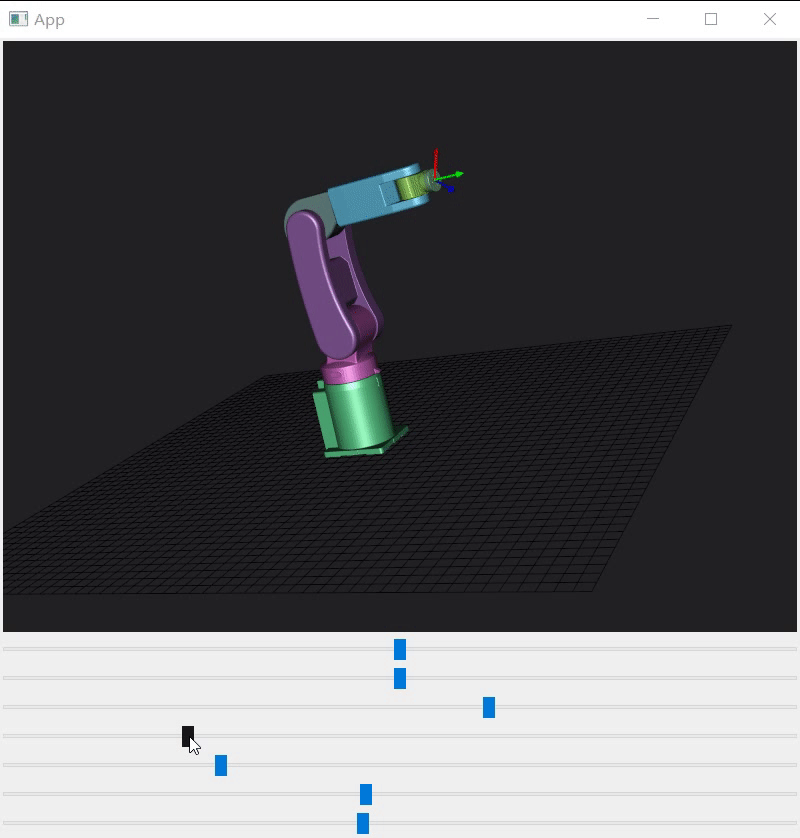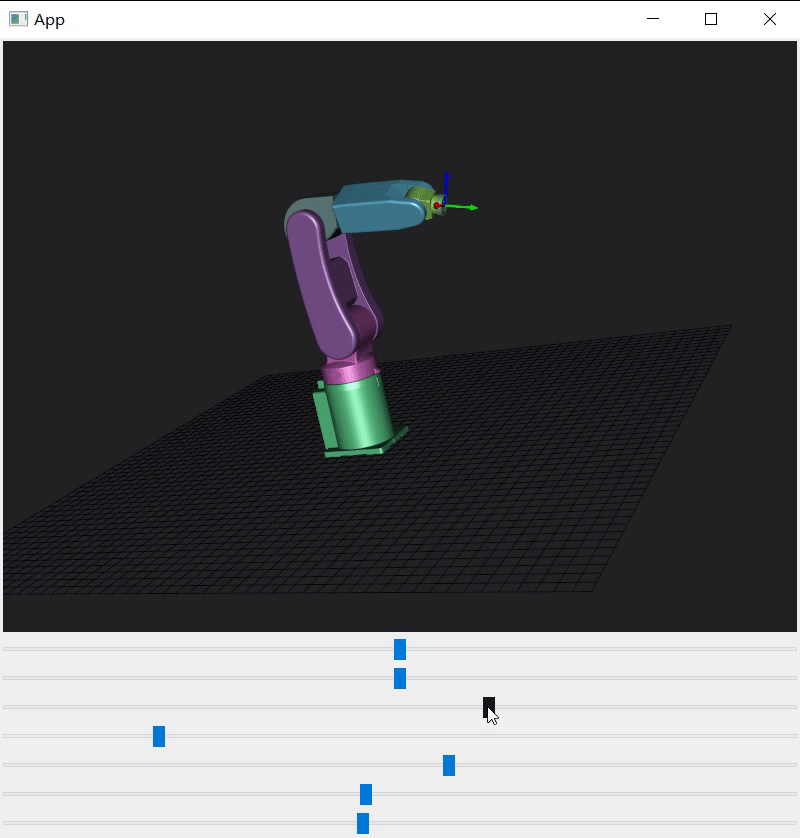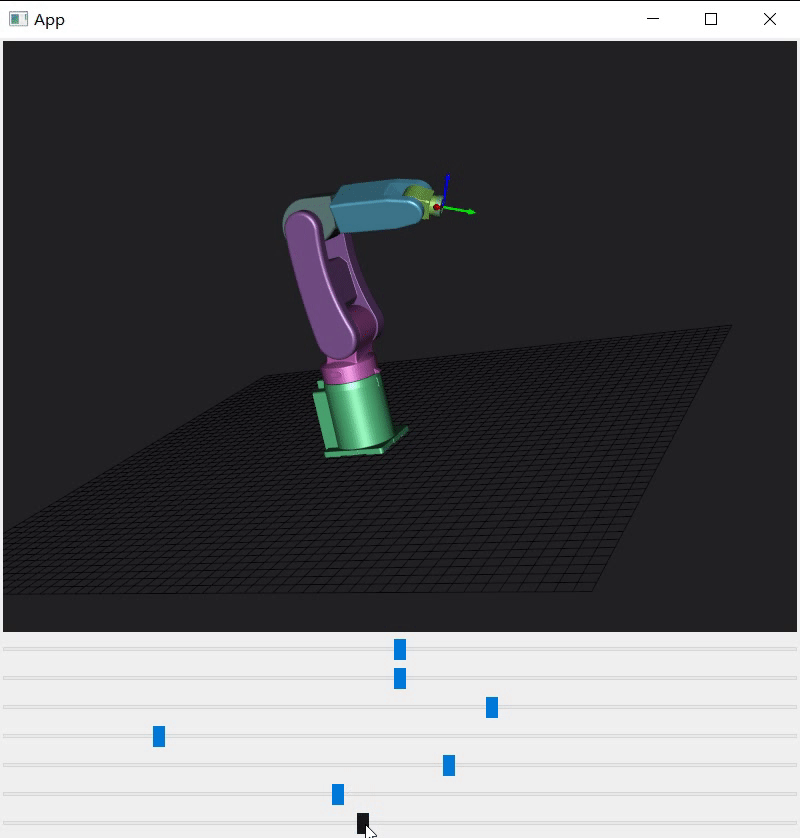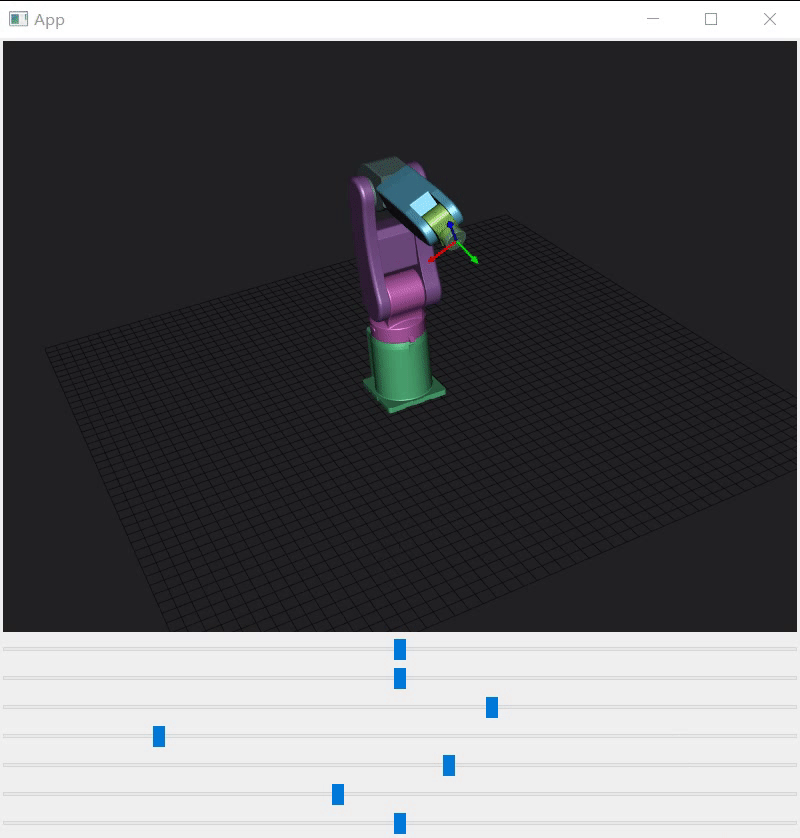
python的代码翻译一遍,根据机械说明书找到每个轴初始角度、允许旋转角度、旋转轴、旋转中心并写成配置文件。
[Parameter]
Joints=7
[Joint0]
file = "RA605_0.stl"
type = Pedestal
color = "#66e299"
Position = "0,0,375"
[Joint1]
file = "RA605_1.stl"
type = RotatingPair
dh = "0,0,0,375"
Range = "-165,165"
color = "#e270d1"
Origin = "0,0,0"
RotateAaxis = "0, 0, 1"
[Joint2]
file = "RA605_2.stl"
type = RotatingPair
dh = "-90,30,-90,0"
Range = "-125,85"
color = "#9e68b5"
Origin = "0,30,0"
RotateAaxis = "1, 0, 0"
[Joint3]
file = "RA605_3.stl"
type = RotatingPair
dh = "0,340,0,0"
Range = "-55,185"
color = "#7a9e9b"
Origin = "0,30,340"
RotateAaxis = "1, 0, 0"
[Joint4]
file = "RA605_4.stl"
type = RotatingPair
dh = "-90,40,0,338"
Range = "-190,190"
color = "#6bcef2"
Origin = "0,0,380"
RotateAaxis = "0, 1, 0"
[Joint5]
file = "RA605_5.stl"
type = RotatingPair
dh = "-90,0,0,0"
Range = "-115,115"
color = "#aaf46d"
Origin = "0,368,380"
RotateAaxis = "1, 0, 0"
[Joint6]
file = "RA605_6.stl"
type = RotatingPair
dh = "-90,0,180,86.5"
Range = "-360,360"
color = "#8ecc9e"
Origin = "0,368,380"
RotateAaxis = "0, 1, 0"
void RobotData::Joint::Rote(const double &angle)
{
if (type != RotatingPair) {
return;
}
static const double M_Zero = 1e-6;
if ((angle - rote_range1) < M_Zero) {
cur_rote_angle = rote_range1;
} else if ((angle - rote_range2) > M_Zero) {
cur_rote_angle = rote_range2;
} else {
cur_rote_angle = angle;
}
assembly->SetOrientation(0, 0, 0);
assembly->RotateWXYZ(cur_rote_angle,
rotate_axis.at(0),
rotate_axis.at(1),
rotate_axis.at(2));
}
vtkSmartPointer<vtkAssembly> RobotData::GetAssembly(const int &id)
{
Q_ASSERT(id < joints_.size());
return joints_[id].assembly;
}
vtkSmartPointer<vtkLODActor> RobotData::GetActor(const int &id)
{
Q_ASSERT(id < joints_.size());
return joints_[id].actor;
}
RobotData::RobotJointType RobotData::JointType2int(const QString &str)
{
if (str == "Pedestal") {
return Pedestal;
} else if (str == "RotatingPair") {
return RotatingPair;
} else if (str == "SlidingPair") {
return SlidingPair;
} else {
return Err;
}
}
void RobotData::SetJointsAngle(QList<double> angle)
{
Q_ASSERT(angle.size() == joints_.size());
for (int i = 0; i < joints_.size(); i++) {
joints_[i].Rote(angle.at(i));
}
}
void RobotData::SetJointAngle(const int &id, const double &angle)
{
Q_ASSERT(id < joints_.size());
joints_[id].Rote(angle);
}
Eigen::MatrixXd RobotData::GetDhParam()
{
return this->mdh_param_;
}
QList<QList<double>> RobotData::GetJointsRoteRange() const
{
QList<QList<double>> result;
foreach (auto joint, joints_) {
result << QList<double> { joint.rote_range1, joint.rote_range2, joint.cur_rote_angle };
}
return result;
}
void RobotData::Initialize()
{
QSettings *config = new QSettings(robot_file_, QSettings::IniFormat);
const int joint_number = config->value("Parameter/Joints").toInt();
const QString file_path = QFileInfo(robot_file_).path();
mdh_param_ = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(joint_number, 4);
for (int i = 0; i < joint_number; i++) {
const QString key = QString("Joint%1").arg(i);
const RobotJointType type = JointType2int(config->value(key + "/type").toString());
const QColor color = QColor(config->value(key + "/color").toString());
const QString file_name = file_path + "/" + config->value(key + "/file").toString();
Joint joint;
joint.type = type;
this->LoadStl(file_name, joint);
this->CreateActor(joint, color);
this->CreateAssembly(joint);
QStringList strs;
if (type == Pedestal) {
strs = config->value(key + "/Position").toString().split(",");
joint.assembly->SetPosition(strs.at(0).toDouble(), strs.at(1).toDouble(), strs.at(2).toDouble());
mdh_param_.row(i) = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(1, 4);
} else if (type == RotatingPair) {
strs = config->value(key + "/Origin").toString().split(",");
joint.assembly->SetPosition(0, 0, 0);
joint.assembly->SetOrigin(strs.at(0).toDouble(), strs.at(1).toDouble(), strs.at(2).toDouble());
strs = config->value(key + "/RotateAaxis").toString().split(",");
joint.rotate_axis = QList<double> { strs.at(0).toDouble(), strs.at(1).toDouble(), strs.at(2).toDouble() };
strs = config->value(key + "/Range").toString().split(",");
joint.rote_range1 = strs.at(0).toDouble();
joint.rote_range2 = strs.at(1).toDouble();
strs = config->value(key + "/dh").toString().split(",");
Eigen::MatrixXd dh(1, 4);
dh << strs.at(0).toDouble() * M_PI / 180.0,
strs.at(1).toDouble(), strs.at(2).toDouble(),
strs.at(3).toDouble() * M_PI / 180.0;
mdh_param_.row(i) = dh;
joint.cur_rote_angle = strs.at(0).toDouble();
}
joints_ << joint;
}
}
void RobotData::LoadStl(const QString &file, RobotData::Joint &joint)
{
vtkNew<vtkSTLReader> reader;
reader->SetFileName(file.toLocal8Bit().data());
reader->Update();
vtkNew<vtkPolyData> vtp;
vtp->DeepCopy(reader->GetOutput());
joint.vtp = vtp;
}
void RobotData::CreateActor(RobotData::Joint &joint, const QColor &diffuse_color)
{
vtkNew<vtkLODActor> actor;
actor->GetProperty()->SetDiffuseColor(
diffuse_color.redF(), diffuse_color.greenF(), diffuse_color.blueF());
actor->GetProperty()->SetDiffuse(.8);
actor->GetProperty()->SetSpecular(.5);
actor->GetProperty()->SetSpecularColor(1, 1, 1);
actor->GetProperty()->SetSpecularPower(30);
vtkNew<vtkPolyDataMapper> mapper;
mapper->SetInputData(joint.vtp);
actor->SetMapper(mapper);
joint.actor = actor;
}
void RobotData::CreateAssembly(RobotData::Joint &joint)
{
vtkNew<vtkAssembly> assembly;
joint.assembly = assembly;
assembly->AddPart(joint.actor);
if (joints_.size() >= 1) {
joints_[joints_.size() - 1].assembly->AddPart(assembly);
}
}
4 正解¶
正解比较简单,自己写一下,跟Matlab结果比较下就可以验证。
Manipulator::Manipulator()
{
Eigen::MatrixXd q_init = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(6, 1); //关节角初始化为[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
setJointAngle(q_init);
Eigen::MatrixXd dh_param(6, 4); //机械臂的DH参数
dh_param << 0, 375, 0, 0,
-M_PI / 2, 0, 30, -M_PI / 2,
0, 0, 340, 0,
0, 338, 40, -M_PI / 2,
0, 0, 0, M_PI / 2,
M_PI, 86.5, 0, -M_PI / 2;
setDhParam(dh_param); //初始化机械臂的DH参数
Manipulator::joint_num = 6;
Manipulator::arm_radius = 0.08; //机械臂连杆的半径(粗细),暂时都按最粗处80mm计算
Manipulator::max_ang = 3 * M_PI / 4 * Eigen::MatrixXd::Ones(Manipulator::joint_num, 1); //最大关节角135°
Manipulator::min_ang = -3 * M_PI / 4 * Eigen::MatrixXd::Ones(Manipulator::joint_num, 1); //最小关节角-135°
}
// 正运动学求解
// 输入六个关节角的大小,输入的是第2、3、5、6个关节处在笛卡尔空间的三维坐标,3×4矩阵。
Eigen::MatrixXd Manipulator::fkine(Eigen::MatrixXd joint_angle)
{ //正运动学
Eigen::MatrixXd joint_position(3, 6);
Eigen::MatrixXd dh = Manipulator::getDhParam();
Eigen::Matrix4Xd T = Eigen::Matrix4Xd::Identity(4, 4);
for (int i = 0; i < joint_angle.rows(); i++) {
double q = dh(i, 0); //关节角
double d = dh(i, 1); //连杆偏距
double a = dh(i, 2); //连杆长度
double alpha = dh(i, 3); //扭转角
Eigen::Matrix4Xd T_temp(4, 4);
T_temp << cos(q), -sin(q) * cos(alpha), sin(q) * sin(alpha), a * cos(q),
sin(q), cos(q) * cos(alpha), -cos(q) * sin(alpha), a * sin(q),
0, sin(alpha), cos(alpha), d,
0, 0, 0, 1;
T = T * T_temp;
joint_position.col(i) = T.block(0, 3, 3, 1);
}
return joint_position;
}
5 逆解¶
自己写的话矩阵运算太恶心了。找了个开源的openrave,其中有一个 ikfast inverse kinematics compiler 模块。
这两个仓库有使用方式,第二个带中文注释。probot_anno_ikfast_manipulator_plugin、LizhiyuanBest/PROBOT_Anno初步试了下,结果是对的,如何集成还没想好。
本来是想给昨天写的MovableAxesWidget搞一个应用场景Demo。结果搞了半天不相关的,现在看来要做UI实现一个简单的示教器才能用到。
要找一个完整的时间来做,先告一段落。元旦再搞,做一个简单的示教器来学习。